Differences, Advantages, and Technical Details: LoRa APRS vs. Meshtastic
LoRa APRS relies on gateways for global connectivity, while Meshtastic creates a true mesh network where nodes forward messages for each other. This makes Meshtastic highly flexible in areas without infrastructure, offering an encrypted, license-free alternative for outdoor and team communication.

LoRa (Long Range) is a powerful radio technology designed for long-distance wireless communication with very low power consumption. It has become popular in many areas, from IoT applications to amateur radio.
In the ham radio context, two systems stand out: LoRa APRS and Meshtastic. Both rely on the same transmission technology, but they follow very different approaches and are aimed at different user groups.
This article highlights the key differences, advantages, and technical details of both systems, and looks at their practical use cases.
Introduction to LoRa APRS
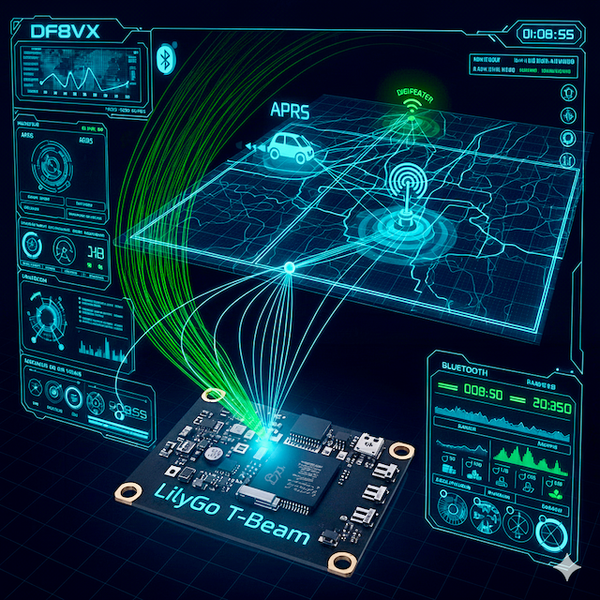
The Automatic Packet Reporting System (APRS) is a digital protocol in amateur radio, used for transmitting position data, telemetry, and short text messages. Originally designed for VHF/UHF radios, it has also been adapted to run over LoRa.
Key Features of LoRa APRS
- Frequency range: mainly 433 MHz (70 cm amateur band)
- Open protocol: freely available for licensed amateurs
- Network integration: can connect to APRS-IS (Internet System)
- Range: several kilometers, depending on antenna and environment
- Unencrypted: encryption is not permitted in amateur radio
- Typical use cases: position tracking, weather stations, telemetry, emergency communications
LoRa APRS is primarily used by licensed amateurs. Gateways receive the radio signals and forward them to the Internet, where they can be visualized in real time, for example on aprs.fi.
Introduction to Meshtastic
Meshtastic is a mesh networking protocol built specifically for license-free LoRa communication. Unlike APRS, it does not rely on central gateways: nodes forward messages to each other, effectively extending the range of the network with every additional participant.
Key Features of Meshtastic
- Frequency ranges: 433 MHz, 868 MHz (Europe), 915 MHz (USA) in ISM bands
- License-free: no amateur radio callsign required
- Encryption: end-to-end with AES-256
- Private groups: closed channels for defined users
- GPS support: nodes with GPS can broadcast position data
- ATAK integration: visualization on tactical maps
- Smartphone connectivity: via Bluetooth and app integration
Meshtastic is especially attractive for outdoor activities, disaster response, and private communications in remote areas. With more than 5,000 nodes already deployed in Europe, the system is rapidly gaining popularity.
Technical Comparison
| Feature | LoRa APRS | Meshtastic |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency range | 433 MHz (ham radio) | 433 MHz, 868 MHz (Europe), 915 MHz (USA) (ISM) |
| License requirement | Yes (amateur radio license) | No (license-free) |
| Encryption | No | Yes (AES-256) |
| Network topology | Point-to-point / Gateway integration | Mesh network |
| Internet integration | APRS-IS possible | Optional via MQTT bridge |
| Position reporting | Yes (APRS format) | Yes (ATAK integration) |
| Smartphone support | Indirect (via gateways) | Yes (via Bluetooth) |
| Typical use | Amateur radio, position reporting | Private groups, disaster response, outdoor communication |
Core difference:
LoRa APRS relies on gateways and APRS-IS for global connectivity, whereas Meshtastic is a true mesh network, where nodes forward messages between each other. This makes Meshtastic far more flexible in areas without infrastructure.
Encryption and Security
One of the biggest differences lies in security:
- LoRa APRS is unencrypted by design, since amateur radio regulations require open and transparent communication. Anyone with the right equipment can receive and decode the data.
- Meshtastic, in contrast, supports AES-256 end-to-end encryption, allowing the creation of secure and private communication channels.
This makes Meshtastic highly suitable for teams, organizations, or tactical operations, where confidentiality is essential. Encrypted position data can also be integrated into mapping tools such as ATAK, which is valuable for search-and-rescue or field operations.
Applications and Use Cases
LoRa APRS – common use cases:
- Position tracking via APRS networks (e.g., aprs.fi)
- Balloon missions and telemetry experiments
- Emergency communications and disaster relief mapping
Meshtastic – common use cases:
- Outdoor communication for hikers, climbers, adventurers
- Tactical use with ATAK integration
- Emergency communication during power or network outages
- Reliable communication in crisis areas with unstable infrastructure
Conclusion
Both LoRa APRS and Meshtastic are powerful systems built on the same LoRa technology, but they differ significantly in target audience, network topology, and security features.
I plan to test both systems in practice, comparing range, network stability, and usability under different conditions.
For licensed hams, LoRa APRS remains a proven way to share data worldwide via APRS-IS. For license-free, encrypted, and flexible networking, however, Meshtastic is quickly becoming a strong alternative, with growing adoption across Europe.